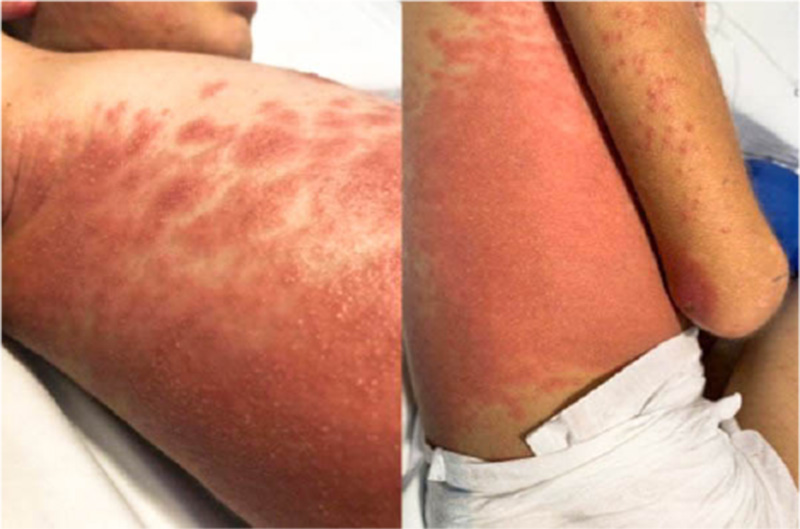
Pustulosis exantemática generalizada aguda en paciente pediátrico polimedicado con traumatismo craneoencefálico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29176/2590843X.1730Palabras clave:
Corticoesteroides, Erupciones por medicamentos, Hipersensibilidad retardada, Pustulosis exantemática generalizada aguda, Unidades de cuidados intensivos pediátricosResumen
La pustulosis exantemática generalizada aguda (PEGA) es una reacción adversa grave caracterizada por el rápido desarrollo de pústulas estériles no foliculares con una base eritematosa (1). Ocurre en 1 a 5 casos por millón de casos por año, con una tasa de mortalidad menor del 5 %; sin embargo, puede presentarse con afectación sistémica y falla orgánica en los casos más severos (2, 3). La principal causa de esta patología es farmacológica.
Presentamos el caso de un paciente con politraumatismo grave que recibió un manejo prolongado con múltiples antibióticos y analgésicos, con el subsecuente desarrollo repentino de una erupción cutánea asociada a prurito, característico de la PEGA. Prontamente se inició manejo con corticosteroides tópicos y la supresión de los posibles desencadenantes; sin embargo, debido a una evolución clínica tórpida con afectación sistémica y severa, se decidió iniciar manejo con corticosteroides sistémicos endovenosos, que lograron finalmente el control de la enfermedad.
Referencias bibliográficas
Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): A review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73(5):843-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.017
Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JNB, Vaillant L, Roujeau J-C. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) - A clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28(3):113-9. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0560.2001.028003113.x
Mockenhaupt M, Viboud C, Dunant A, Naldi L, Halevy S, Bouwes Bavinck JN, et al. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: assessment of medication risks with emphasis on recently marketed drugs. The EuroSCAR-Study. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128(1):35-44. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5701033
Gordon J. Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis: An Uncommon Cause of Fever and Rash. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(3):681.e1-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2015.06.063
Salinas J. Mecanismos de daño inmunológico. Rev Med Clin Las Condes. 2012;23(4):458-463. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0716-8640(12)70336-X
Hoetzenecker W, Nägeli M, Mehra ET, Jensen AN, Saulite I, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, et al. Adverse cutaneous drug eruptions: current understanding. Semin Immunopathol. 2016;38(1):75-86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-015-0540-2
Álvaro-Vásquez J, Bernabé-Del Río C, Esther Maya Aranda S, Espinosa-Tavitas MI. Pustulosis exantemática generalizada aguda inducida por ceftriaxona. Med Cutan Iber Lat Am. 2016;44(3):216-20.
Roujeau JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Bourseau C, Guillaume JC, Bernard P, Lok C, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127(9):1333-8.
Dibek Misirlioglu E, Guvenir H, Bahceci S, Haktanir Abul M, Can D, Usta Guc BE, et al. Severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions in pediatric patients: a multicenter study. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017;5(3):757-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2017.02.013
Rosen A, Del Paggio JC, Chan B, Abu-Abed S, Rawls M, Ellis AK. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis with multisystem manifestations: Pinpoint pustules and purulent lakes. Ann Allergy, Asthma Immunol. 2018;120(1):92-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2017.09.077
Speeckaert MM, Speeckaert R, Lambert J, Brochez L. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: an overview of the clinical, immunological and diagnostic concepts. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20(4):425-33. https://doi.org/10.1684/ejd.2010.0932
Cranga TA, Simpson MA, Featherstone P. Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)-a potential pitfall for the acute physician. Acute Med. 2016;15(3):140-4.
DaCunha M, Moore S, Kaplan D. Cephalexin-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Dermatol Reports. 2018;10(2):7686. https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2018.7686
Chu CY. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). UpT
Ross CL, Shevchenko A, Mollanazar NK, Hsu S, Motaparthi K. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to terbinafine. Dermatol Ther. 2018;31(4):e12617. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.12617
Kumar V, Kalaiselvan V, Kumar AP, , Saurabh A, Thota P, Sidhu S, et al. Cefixime-associated acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: Rare cases in India. Indian J Pharmacol. 2018;50(4):204-7. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijp.IJP_673_17
Thienvibul C, Vachiramon V, Chanprapaph K. Five-Year Retrospective Review of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis. Dermatol Res Pract. 2015;2015:260928. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/260928
Velter C, Schissler C, Moulinas C, Tebacher-Alt M, Siedel JM, Cribier B, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis caused by an iodinated contrast radiocontrast medium for computed tomography arthrography of the knee. Contact Dermatitis. 2017;76(6):371-3. https://doi.org/10.1111/cod.12724
Sáenz de Santa María García M, Noguerado Mellado B, Rojas Pérez-Ezquerra P, Hernandez Aragües I, de Barrio Fernández M. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis due to diltiazem: Investigation of cross-reactivity with other calcium channel blockers. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016;4(4):765-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2016.02.004
Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bouwes Bavinck JN, Naldi L, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)—results of a multinational case–control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007;157(5):989-96. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08156.x
Mustafa SS, Ostrov D, Yerly D. Severe Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions: Presentation, Risk Factors, and Management. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018;18(4):26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-018-0778-6
Cómo citar
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2022 Revista de la Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología y Cirugía Dermatológica

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.

| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |