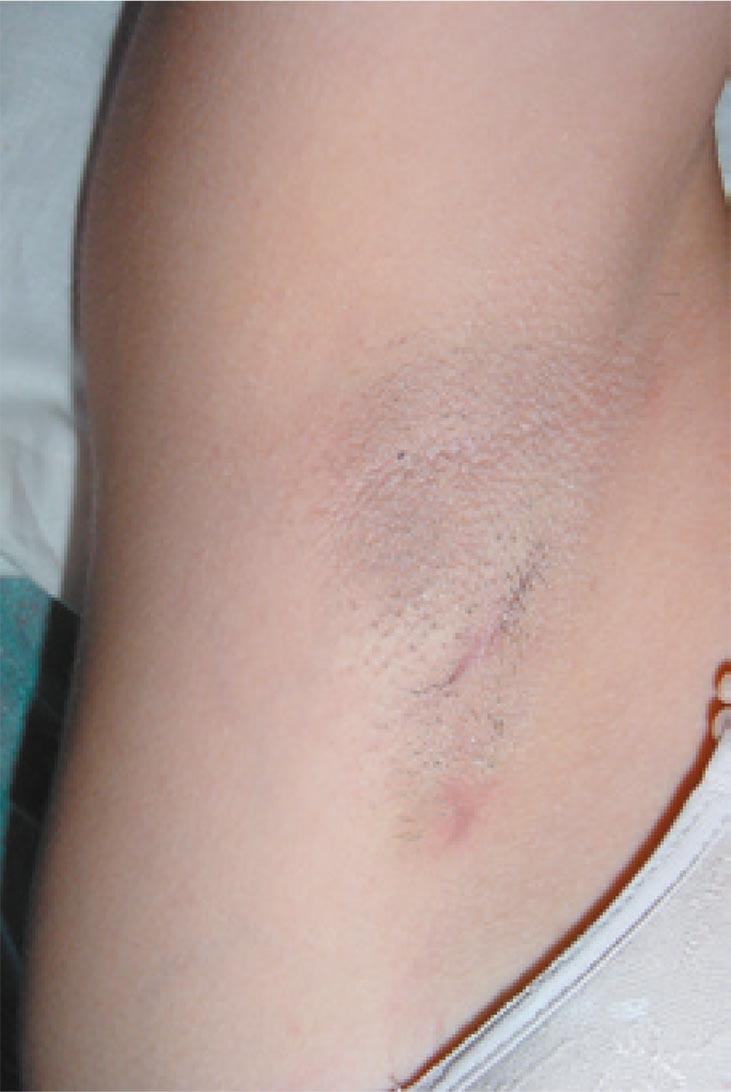
Curetaje subcutáneo en el manejo de la hiperhidrosis axilar
Palabras clave:
Hiperhidrosis, axilar, curetaje, subcutáneoResumen
SE PRESENTA el caso de un paciente con hiperhidrosis axilar exitosamente tratado con curetaje subcutáneo y se discuten las ventajas de esta técnica en comparación con otras opciones terapéuticas disponibles en la actualidad.
Biografía del autor/a
Ana Milena Toro
R II Dermatología, Universidad Pontifi cia Bolivariana
Luz Marina Gómez
Dermatóloga, Jefe de Posgrado en Dermatología, Universidad Pontifi cia Bolivariana, Medellín – Colombia
Referencias bibliográficas
2. Lonsdale- Eccles A, Leonard N, Lawrence C. Axillary hyperhidrosis: eccrine or apocrine? Clin Exp Dermatol 2003; 28: 2 – 7.
3. Gómez F, Gómez LM, Hiperhidrosis axilar: un nuevo método de tratamiento y revisión de la literatura. Revista Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología 1991;1:54 – 57.
4. Langtry JA, Hyperhidrosis. En: Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Berth-Jones J, et al. Treatment of skin disease comprehensive therapeutic strategies 2ed. Elsevier Mosby. 2006. 288 – 91.
5. Bisbal J, Del Cacho C, Casalots J. Surgical treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis. Ann Plast Surg 1987; 18: 429– 36.
6. Herbst F, Plas EG, Fuggo R, Fritsch A. Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary hyperhidrosis of the upper limbs: a critical análisis and longterm results of 480 operations. Ann Surg 1994; 220: 86 – 90.
7. Rompel R, Peros I, Petres J, Subcutaneous curettage for the treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis. Eur J Dermatol 1997; 7: 43 – 6.
8. Rompel R, Scholz S, Subcutaneous Curetaje vs. Injection of botulinum toxin A for treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis. JEADV 2001; 15: 207 – 11.
9. Beer GM, Baumüller S, Zech N, Wyss P, Strasser D, Varga Z., et al. Immunohistochemical differentiaton and localization analysis of sweat glands in the adult human axilla. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006; 117: 2043 – 2049
Cómo citar
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |