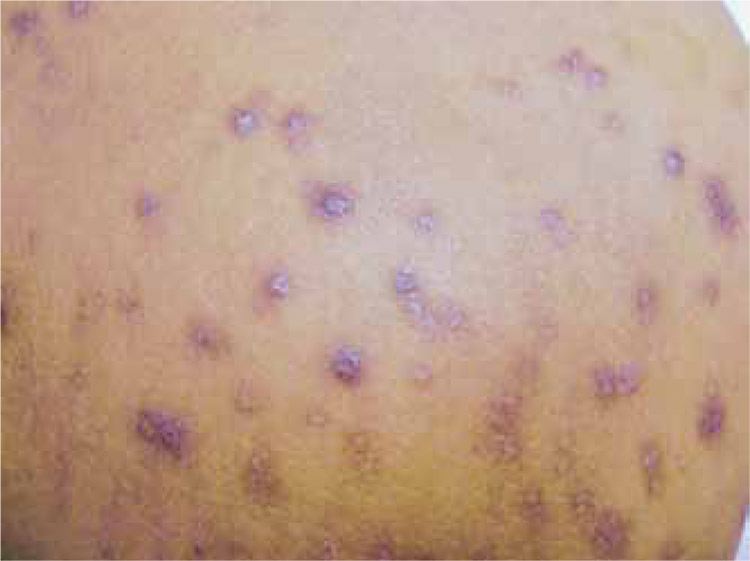
Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis
Keywords:
Diseases, diabetes mellitus, allopurinolAbstract
Acquired perforating disorders are a group of diseases that share some clinical manifestations such as umbilicated papules or keratotic nodules, chronic itching and Koebner phenomenon; they also show pathological changes such as routes or tunnels through which collagen bands are eliminated.
The differential diagnosis is quite broad and it might be more complicated to focus on patients with skin types IV to VI as it was in the case of our patient, however, if there is a history of diabetes mellitus or renal disease, this diagnosis should be taken into account.
Author Biographies
Claudia Patricia Palacios
Médica, residente de Dermatología, Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia
María Isabel Arredondo
Médica dermatóloga, Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe, Medellín, Colombia
Luz Adriana Vásquez
Médica dermatóloga, Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe, Medellín, Colombia
Verónica Molina
Médica dermatóloga, Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe, Medellín, Colombia
Juan Esteban Arroyave
Médico dermatólogo, Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe, Medellín, Colombia
Rodrigo Restrepo
Médico, dermatopatólogo; docente, Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia
References
2. Tsuboi H, Katsuoma K, Characteristics of acquired reactive perforating Collagenosis. J Dermatol. 2007;34:640-4.
3. Satti MB, Aref AH, Raddadi AA, Al Ghamdi FA. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: A clinicopathologic study of 15 cases from Saudi Arabia. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24:223-7.
4. Thiele-Ochel S, Schneider LA, Reinhold K, Hunzelmann N, Krieg T, Scharffetter-Kochanek K. Acquired perforating collagenosis: Is it due to damage by scratching? Br J Dermatol. 2001;145:173-4.
5. Gambichler T, Birkner L, Stücker M, Othlinghaus N, Altmeyer P, Kreuter A. Up-regulation of transforming growth factor-beta3 and extracellular matrix proteins in acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:463-9.
6. Faver IR, Daoud MS, Su WPD. Acquired perforating collagenosis. Report of six cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30:575-80.
7. Satchell AC, Crotty K, Lee S. Reactive perforating collagenosis: A condition that may be underdiagnos. Australas J Dermatol. 2001;42:284-7.
8. Basak P, Turkmen C. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. Eur J Dermatol. 2001;11:466-8.
9. Ghosh SK, Bandyopadhyay D, Chatterjee G. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis following insect bite. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:306-7.
10. Karpouzis A, Gitromanolaki A, Sivridis E,Kouskoukis C. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: Current status. J Dermatol. 2010;37:585-92.
How to Cite
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |