Skin microbiota: The cutaneous ecosystem
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29176/2590843X.261Keywords:
microbiota, ecosystem, microbiology, skin floraAbstract
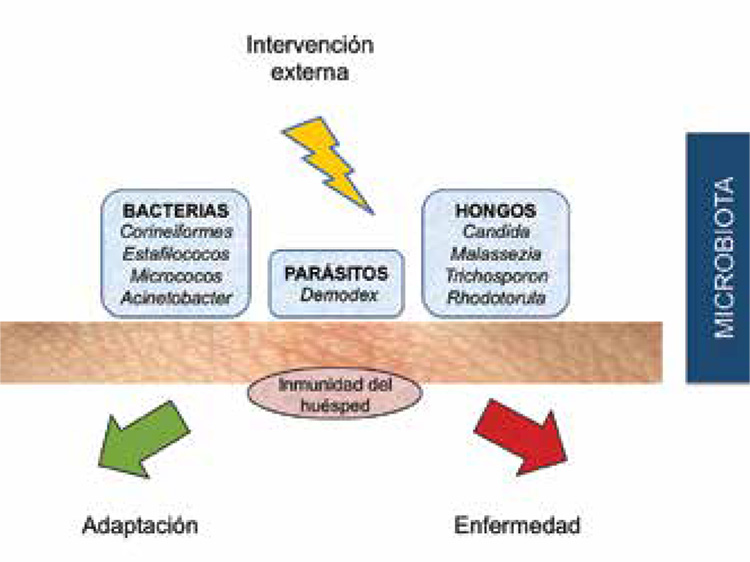
In the skin surface cohabite bacteria, fungi and parasites; these microbes constitute a complex ecosystem which is in constant interaction with the host. This ecosystem is actively involved in the double protective function of the skin, as a physical and immunological barrier. When the balance of the ecosystem is disturbed, it has negative consequences and predisposes to disease.
In this review, we describe the characteristics of the ecosystem of the skin, the skin micriobiota composition, its variability and the physiological basis of their main interactions.
Author Biographies
Luz Angélica Patiño
Médica, residente de segundo año de Dermatología, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad CES, Medellín, Colombia; Centro Dermatológico Federico Lleras Acosta, E.S.E., Bogotá, D.C., Colombia.
Camilo Andrés Morales
Médico dermatólogo, Oficina de Docencia e Investigación, Centro Dermatológico Federico Lleras Acosta, E.S.E., Bogotá, D.C., Colombia; instructor, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad CES, Medellín, Colombia.
References
2. Navarro FA. Glosario dermatológico de dudas inglés-español (1ª parte): A-F. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 1999;90:327-38.
3. Prats G. Los microbios y la enfermedad. En: Prats G. Microbiología clínica. Primera edición. Madrid: Editorial Médica Panamericana; 2006. p. 1-14.
4. Kong HH, Segre JA. Skin microbiome: Looking back to move forward. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;13:933-9.
5. Kligman AM, Leyden JJ, McGinley KJ. Bacteriology. J Invest Dermatol. 1976;67:160-8.
6. Marples MJ. Life on the human skin. Sci Am. 1969;220:108-15.
7. Fredricks DN. Microbial ecology of human skin in health and disease. J Invest Dermatol Symp Proc. 2001;6:167-9.
8. Grice EA, Segre JA. The skin microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9:244-53.
9. Zhao L. Genomics: The tale of our other genome. Nature. 2010;465:879-80.
10. Kong HH. Skin microbiome: Genomics-based insights into the diversity and role of skin microbes. Trends Mol Med. 2011;17:320-8.
11. Cogen AL, Nizet V, Gallo RL. Skin microbiota: A source of disease or defence? Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:442-55.
12. Verhulst NO, Qiu YT, Beijleveld H, Maliepaard C, Knights D, Schulz S. Composition of human skin microbiota affects attractiveness to malaria mosquitoes. PLoS One. 2011;6:e28991.
13. De Jong R, Knols BG. Selection of biting sites on man by two malaria mosquito species. Experientia. 1995;51:80-4.
14. Roth RR, James WD. Microbiology of the skin: Resident flora, ecology, infection. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989;20:367-90.
15. Reid G, Younes JA, van der Mei HC, Gloor GB, Knight R, Busscher HJ. Microbiota restoration: Natural and supplemented recovery of human microbial communities. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9:27-38.
16. Hoffjan S, Stemmler S. On the role of the epidermal differentiation complex in ichthyosis vulgaris, atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:441-9.
17. Gambichler T, Boms S, Stucker M, Kreuter A, Moussa G, Sand M, et al. Epidermal thickness assessed by optical coherence tomography and routine histology: Preliminary results of method comparison. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:791-5.
18. Mourelatos K, Eady EA, Cunliffe WJ, Clark SM, Cove JH. Temporal changes in sebum excretion and propionibacterial colonization in preadolescent children with and without acne. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:22-31.
19. Pessanha B, Farb A, Lwin T, Lloyd B, Virmani R. Infectious endocarditis due to Corynebacterium xerosis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2003;12:98-101.
20. Bierbaum G, Götz F, Peschel A, Kupke T, van de Kamp M, Sahl HG. The biosynthesis of the lantibiotics epidermin, gallidermin, Pep5 and epilancin K7. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek.1996;69:119-27.
21. Wächtler B, Citiulo F, Jablonowski N, Förster S, Dalle F, Schaller M, et al. Candida albicans-epithelial interactions: Dissecting the roles of active penetration, induced endocytosis and host factors on the infection process. PLoS One. 2012;7:e36952.
22. Waggoner-Fountain LA, Walker MW, Hollis RJ, Pfaller MA, Ferguson JE 2nd, Wenzel RP, et al. Vertical and horizontal transmission of unique Candida species to premature newborns. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:803-8.
23. Ashbee HR. Update on the genus Malassezia. Med Mycol. 2007;45:287-303.
24. Prohic A, Kasumagic-Halilovic E. Identification of Malassezia pachydermatis from healthy and diseased human skin. Med Arh. 2009,63:317-9.
25. Hernández FH, Javier L, Tovar M, Mora EB, López AA. Especies de Malassezia asociadas a diversas dermatosis y a piel sana en población mexicana. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2003;52:141-4.
26. Gaitanis G, Chasapi V, Velegraki A. Novel application of the masson-fontana stain for demonstrating Malassezia species melanin-like pigment production in vitro and in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 2005;43:4147-51.
27. Akaza N, Akamatsu H, Sasaki Y, Takeoka S, Kishi M, Mizutani H, et al. Cutaneous Malassezia microbiota of healthy subjects differ by sex, body part and season. J Dermatol. 2010;7:786-92.
28. Chagas-Neto TC, Chaves GM, Colombo AL. Update on the genusTrichosporon. Mycopathologia. 2008;166:121-32.
29. Biasoli MS, Carlson D, Chiganer GJ, Parodi R, Greca A, Tosello ME, et al. Systemic infection caused by Trichosporon asahii in a patient with liver transplant. Med Mycol. 2008;46:719-23.
30. Shinde RS, Mantur BG, Patil G, Parande MV, Parande AM. Meningitis due to Rhodotorula glutinis in an HIV infected patient. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2008;26:375-7.
31. de Rojas M, Riazzo C, Callejón R, Guevara D, Cutillas C. Morphobiometrical and molecular study of two populations of Demodex folliculorum from humans. Parasitol Res. 2012;110:227-33.
32. Kligman AM, Christensen MS. Demodex folliculorum: Requirements for understanding its role in human skin disease. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:8-10.
33. Lacey N, Kavanagh K, Tseng SC. Under the lash: Demodex mites in human diseases. Biochem (Lond). 2009;31:2-6.
34. Meyer T, Stockfleth E, Christophers E. Immune response profiles in human skin. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:1-7.
35. Schauber J, Gallo RL. Antimicrobial peptides and the skin immune defense system J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008;122:261-6.
36. Chamorro CI, Weber G, Grönberg A, Pivarcsi A, Stahle M. The human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 suppresses apoptosis in keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:937-44.
37. Krishna S, Miller LS. Innate and adaptive immune responses against Staphylococcus aureus skin infections. Semin Immunopathol. 2012;34:261-80.
38. Yamasaki K, Schauber J, Coda A, Lin H, Dorschner RA, Schechter NM, et al. Kallikrein-mediated proteolysis regulates the antimicrobial effects of cathelicidins in skin. FASEB J. 2006;20:2068-80.
39. Schroeder BO, Wu Z, Nuding S, Groscurth S, Marcinowski M, Beisner J, et al. Reduction of disulphide bonds unmasks potent antimicrobial activity of human beta-defensin 1. Nature. 2011;469:419-23.
40. Abtin A, Eckhart L, Gläser R, Gmeiner R, Mildner M, Tschachler E, et al. The antimicrobial heterodimer S100A8/S100A9 (calprotectin) is upregulated by bacterial flagellin in human epidermal keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:2423-30.
41. Maerki C, Meuter S, Liebi M, Mühlemann K, Frederick MJ, Yawalkar N, et al. Potent and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity of CXCL14 suggests an immediate role in skin infections. J Immunol. 2009;182:507-14.
42. Lai Y, Di Nardo A, Nakatsuji T, Leichtle A, Yang Y, Cogen AL, et al. Commensal bacteria regulate Toll-like receptor 3-dependent inflammation after skin injury. Nat Med. 2009;15:1377-82.
43. Bastos MC, Ceotto H, Coelho ML, Nascimento JS. Staphylococcal antimicrobial peptides: Relevant properties and potential biotechnological applications. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2009;10:38-41.
How to Cite
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |