Manifestaciones cutáneas de las neoplasias malignas
Palabras clave:
N eoplasia, manifestaciones cutáneas, diagnósticoResumen
Las manifestaciones cutáneas de los tumores malignos comprenden un grupo de enfermedades que pueden ser marcadores de la presencia de neoplasias ocultas y permitir su diagnóstico temprano. Su fisiopatología aún no ha sido bien esclarecida. Existen diversos grupos, algunos claramente asociados y otros en los que sólo hay una asociación estadística.
Biografía del autor/a
Karen Zapata
Residente II de Dermatología, Universidad del Valle, Cali, Colombia
Ana Francisca Ramírez
Dermatóloga, Dermatología Oncológica, Hospital Universitario del Valle.
Referencias bibliográficas
2. Schwartz RA. Cutaneous markers of internal malignancy. En: Schwartz RA, editor. Skin cancer recognition and management. New York: Springer Verlag; 1988. p.194-225.
3. Hall TC. Paraneoplasic syndromes: mechanism. Semin Oncol. 1997;24:269-76.
4. Finn OJ. Molecular origins of cancer immunology. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2704-15.
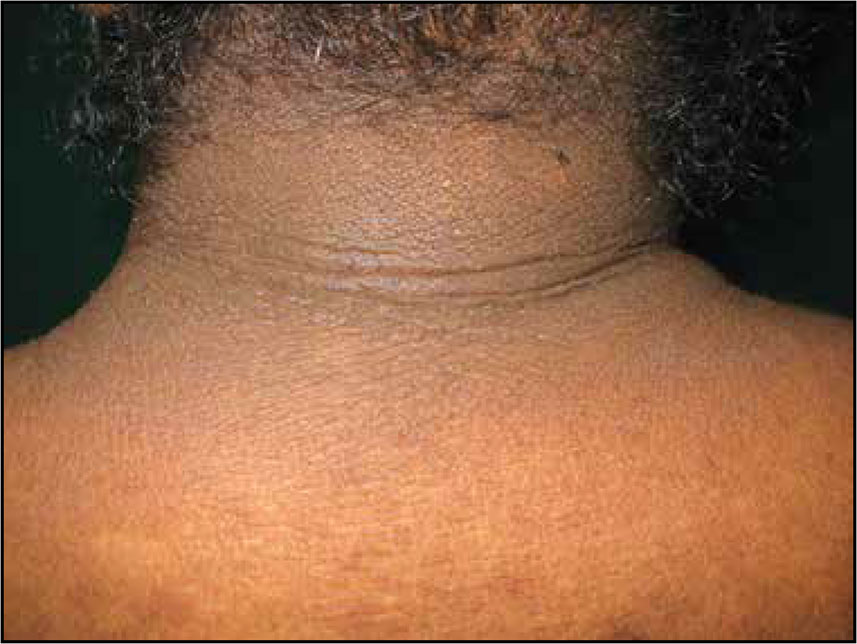
5. Sedano HO, Gorlin RJ. Acanthosis nigricans. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1987;63:462-7.
6. Brown J, Winkelmann RK. Acanthosis nigricans: a study of 90 cases. Medicine. 1968;47:33-51.
7. Curth HO. Cancer associated with acantosis nigicans. Arch Surg. 1943;47:517-52.
8. Braverman IM. Skin manifestations of internal malignancy. Clin Geriatr Med. 2002;1:1-19.
9. Pipkin CA, Lio PA. Cutaneous manifestations of internal malignancies: An overview. Dermatol Clin. 2008;26:1-15.
10. Moore RL, Devere TS. Epidermal manifestations of internal malignancy. Dermatol Clin. 2008;26:17-29.
11. Breathnach SM, Wells GC. Acanthosis palmaris: tripe palms. A distinctive pattern of palmar keratoderma frequently associated with internal malignancy. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1980;5:181-9.
12. Clarke J. Malignant acanthosis nigricans. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1977;2:167-70.
13. Dantzig PI. Sign of Leser-Trélat. Arch Dermatol .1973;108:700-1.
14. Yaniv R, Servadio Y, Feinstein A, Trau H. The sign of LeserTrélat associated with transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder - a case report and short review. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1994;19:142-5.
15. Ellis DL, Yates RA. Sign of Leser-Trélat. Clin Dermatol. 1993;11:1-19.
16. Ellis DL, Kafka SP, Chow JC, Nanney LB, Inman WH, McCadden ME, et al. Melanoma grow factors, acanthosis nigricans, the sign of Leser-Trélat and multiple acrochordons. A posible role for alpha growth factor in cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:1582-7.
17. Chosidow O, Becherel PA, Piette JC, Arock M, Debré P, Frances C. Tripe palms associated with systemic mastocytosis: The role of transforming growth factor –alpha and efficacy of interferon-alpha. Br J Dermatol. 1998;138:698-703.
18. Howel-Evans W, McConnell RB, Clarke CA, Sheppard PM. Carcinoma of the esophagus with keratosis palmaris et plantaris (tylosis): a study of two families. Q J Med. 1958;27:413-29.
19. Stevens HP, Kelskll DP, Leigh IM, Ostlere LS, Macdermot KD, Rustin MH. Punctate palmoplantar keratoderma and malignancy in a four generation family. Br J Dermatol. 1996;134:720-6.
20. Basex A, Griffiths A. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica- a new cutaneous marker of malignancy. Br J Dermatol. 1980;103:301-6.
21. Gougerot H, Rupp C. Dermatose érythémato-squameuse avec hyperkératose palmo-plantaire, porectasies digitales et cancer de la langue latent. Contribution á l’étude des dermatoses monitrices de cancer. Paris Med. 1922;43:234-7.
22. Karabulut AA, Ayse A, Sahin S, Sahin M, Eksioglu M, Üstün H. Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis of Bazex (Bazex’s syndrome): report of a female case associated with cholangiocarcinoma and review of the published work. J Dermatol. 2006;33:850-4.
23. Bolognia JL, Brewer YP, Cooper DL. Bazex syndrome (acrokeratosis paraneoplastica). An analytic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 1991;70:269-80.
24. Sarkar B, Knecht R, Sarkar C, Weidauer H. Bazex syndrome (acrokeratosis paraneoplastica ). Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1998;255:205-10.
25. Ronchese, F. Ichthyosiform atrophy of the skin in Hodgkin’s disease. Arch Dermatol Syphilol. 1943;47:778-81.26. Sneddon IB. Adquired icthyosis in Hodgkin’s disease. Br Med J. 1955;26:763.
27. Majekodumni AE, Femi-Pearse D. Icthyosis: early manifestation of intestinal leiomyosarcoma. Br Med J. 1974;3:724.
28. Santos-Juanes J, Palomo C, Galache C, Costas C, Curto JR, Sánchez del Río J, et al. Linfoma anaplásico de células grandes sociadas a ictiosis adquirida. Med Cutan Iber Lat Am. 2003;31:187-91.
29. Weenig RH, Mehrany K. Dermal and pannicular manifestations of internal malignancy. Dermatol Clin. 2008;26:31-43.
30. Sweet RD. An acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis. Br J Dermatol. 1964;76:349-56.
31. Fett DL, Gibson LE, Su WP. Sweet’s syndrome: systemic signs and symptoms and associated disorders. Mayo Clin Proc. 1995;70:234-40.
32. Brunsting LA, Goeckerman WH, O’ Leary PA. Pyodema (ecthyma) gangrenosum: clinical and experimental observation in five cases occurring in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1930;20:655-80.
33. Gibson LE, El- Azhary R. Erythema elevatum diutinum. Clin Dermatol. 2000;18:295.
34. Gottron HA. Skleromyxodem (eine eigenartige euscheinugsform von myxothesaurodermie). Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1954;199:71-9.
35. Bushke A. Ueber Scleroedem. Berlin Klinische Wochenschrift. 1902;39:955-6.
36. Barrow MV, Holubar K. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis. A review of 33 patients. Medicine (Baltimore).1969;48:287-305.
37. Kossard S, Winkelman RK. Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128:94-100.
38. Bardwick PA, Zvaifler NJ, Gill GN, Newman D, Greenway DL, Resnick DL. Plasma cell dyscrasia with polineuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, M protein and skin changes: the POEMS syndrome. Report on two cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 1980;59:311-22.
39. Soubrier MJ, Jean-Jacques D, Sauvezie BJM. POEMS syndrome: a study of 25 cases and review of the literature. Am J Med. 1994;97:543-53.
40. Zea-Mendoza A, Alonso-Ruiz A, García-Vadillo A, et al. POEMS syndrome with neuroarthropathy and nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver. Arthritis Rheum. 1984; 27:1053-7.
41. El Tal AK, Tannous Z. Cutaneous vascular disorders associated with internal malignancy. Dermatol Clin. 2008;26:45-57.
42. Tang L, His M, Rye S, Minauchi Y. Syndrome of polyneuropathy, skin hyperpigmentation, edema and hepatosplenomegaly. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. 1983; 46: 1108-14.
43. El Tal AK, Tannous Z. Cutaneous vascular disorders associated with internal malignancy. Dermatol Clin. 2008;26:45-57.
44. Thomas I, Schwartz R. Cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes: uncommon presentations. Clin Dermatol. 2005;23:593-600.
45. Tan E, Tan S, RCPath D, Ng SK. Cutaneous mucinosis in derm tomyositis associated with a malignant tumor. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;48:S41-2.
46. Ahmed AR, Avram MM, Duncan LM. A 79 year old woman with gastric lymphoma and erosive and cutaneous lesions. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:382-91.
47. Hinds G, Thomas V. Malignancy and cancer treatment-related hair and nail changes. Dermatol Clin. 2008;26:59-68. 48. Vulink AJ, Bokkel DT, Huinink D. Acquired hypertrichosis lanuginosa: a rare cutaneous paraneoplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1625-6.
49. Mlczoch L, Attarbaschi A, Dworzak M, Gadner H, Mann G. Alopecia areata and multifocal bone involvement in a young adult with Hodgkin’s disease. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46:623-7.
50. Crotty K, McCarthy W, Quinn M, McCarthy S. Alopecia neoplastica caused by desmoplastic melanoma. Aust J Dermatol. 2003; 44: 295-8.
Cómo citar
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |