Epidermolysis bullosa in Colombia: 10 years of experience.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29176/2590843X.1674Keywords:
Epidermólisis ampollosa, desenlaces, diagnóstico, demografíaAbstract
Objective: to describe the epidemiological, sociodemographic, clinical characteristics and diagnostic methods of patients with a diagnosis of BE, linked to the DEBRA Colombia foundation.
Materials and Methods: An observational, descriptive and retrospective cross-sectional study where the patients evaluated at the DEBRA foundation were characterized in the period 2009-2020.
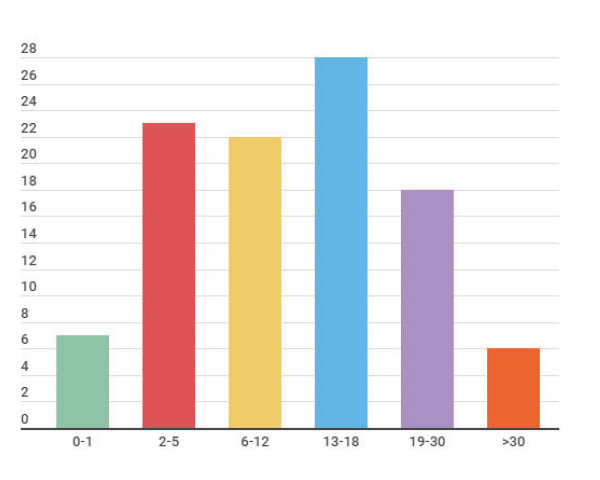
Results: A total of 104 patients were registered, with a male / female ratio of 1: 1.5, the majority aged between 13 and 18 years at the time of the study. 63.5% of the patients are active at the cut-off date. Of the total number of patients, 98 came from Colombia and 6 patients came from Venezuela. 51.9% belonged to strata 1 and 2 and 14.4% belonged to strata 3 and 4. 34.6% of the patients belonged to the contributory regime and 35.6% to the subsidized regime. In the population studied, 47% of the patients have a diagnosis of DEB, followed by 29.8% EBS. The form of diagnosis is clinical in most cases, with genetic confirmation only in 31.7%, the most frequent mutation was c.6781C> T, p. Arg2261Ter mainly associated with the deficit of COL7A1.
Conclusions: In this review we present 104 patients with BE in Colombia, registered in the DEBRA Colombia foundation. It is the largest number of reported patients, however, it cannot represent the totality of BE patients in the country. The most frequent clinical form was DEB in the study population. Also a third of the analyzed sample had a genetic diagnosis. In addition to skin involvement, the majority of patients present involvement in the oral cavity, hematological digestive tract, nutrition, among others.
Author Biographies
Mauricio Torres-Pradilla, Fundación Universitaria de Ciencias de la Salud
Dermatólogo pediatra, coordinador del posgrado de Dermatología. Fundación Universitaria de Ciencias de la Salud - Hospital de San José de Bogotá.
Mauricio Chaves, Fundación DEBRA Colombia
Epidemiólogo clínico, Fundación DEBRA Colombia.
Elvis Gomez, FUCS
Residente de tercer año de Dermatología. Fundación Universitaria de Ciencias de la Salud - Hospital de San José de Bogotá.
Andrés Villamil, Hospital de San José de Bogotá
Estudiante de Medicina. Fundación Universitaria de Ciencias de la Salud - Hospital de San José de Bogotá
Liliana Consuegra-Bazzani, Fundación DEBRA Colombia
Fundadora y directora, Fundación DEBRA Colombia.
References
Siañez-González C, Pezoa-Jares R, Salas-Alanis J. Epidermólisis ampollosa congénita: revisión del tema. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2009;100(10):842-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-7310(09)72912-6
Has C, Fischer J. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: New diagnostics and new clinical phenotypes. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28(10):1146-52. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.13668
Uitto J, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Christiano AM, McGrath JA, Has C, South AP, et al. Progress toward Treatment and Cure of Epidermolysis Bullosa: Summary of the DEBRA International Research Symposium EB2015. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136(2):352-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2015.10.050
Torres R, Palomo P, Torres G, Lipa R. [Epidermolysis bullosa in Peru: clinical and epidemiological study of patients treated in a national reference pediatric hospital, 1993-2015]. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Publica. 2017;34(2):201-8 https://doi.org/10.17843/rpmesp.2017.342.2484
Fine JD, Johnson LB, Weiner M, Li KP, Suchindran C. Epidermolysis bullosa and the risk of life-threatening cancers: the National EB Registry experience, 1986-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(2):203-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2008.09.035
Riedl R, Dart J. Patient organizations and the investigative dermatology community as partners: DEBRA and Epidermolysis bullosa research. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133(9):2116-7. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2013.257
Shinkuma S, Natsuga K, Nishie W, Shimizu H. Epidermolysis bullosa in Japan. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28(2):431-2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2010.02.010
Kim WB, Alavi A, Walsh S, Kim S, Pope E. Epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa: a systematic review exploring genotype-phenotype correlation. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2015;16(2):81-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-015-0119-7. PMID: 2569095
Fine JD, Johnson LB, Weiner M, Suchindran C. Cause-specific risks of childhood death in inherited epidermolysis bullosa. J Pediatr. 2008;152(2):276-80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.06.039
Hon KL, Li JJ, Cheng BL, Luk DC, Murrell DF, Choi PC, et al. Age and etiology of childhood epidermolysis bullosa mortality. J Dermatol Treat. (2015;26(2):178-82. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546634.2014.915002
Prodinger C, Reichelt J, Bauer JW, Laimer M. Epidermolysis bullosa: Advances in research and treatment. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28(10):1176-89. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.13979
Tang JY, Marinkovich MP, Lucas E, Gorell E, Chiou A, Lu Y, et al. A systematic literature review of the disease burden in patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021;16(1):175. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-021-01811-7
Guillen-Climent S, Fernández García L, GarcíaVázquez A, Martín JM. Hereditary Epidermolysis Bullosa: A Case Series. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2021;S0001-7310(21)00165-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ad.2020.08.015
Liy-Wong C, Cepeda-Valdes R, Salas-Alanis JC. Epidermolysis bullosa care in Mexico. Dermatol Clin. 2010;28(2):393-4, xiii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2010.02.014
Baardman R, Yenamandra VK, Duipmans JC, Pasmooij AMG, Jonkman MF, van den Akker PC, et al. Novel insights into the epidemiology of epidermolysis bullosa (EB) from the Dutch EB Registry: EB more common than previously assumed? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35(4):995-1006. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.17012
Alharthi R, Alnahdi MA, Alharthi A, Almutairi S, Al-Khenaizan S, AlBalwi MA. Genetic Profile of Epidermolysis Bullosa Cases in King Abdulaziz Medical City, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Front Genet. 2022;12:753229. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.753229
How to Cite
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista de la Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología y Cirugía Dermatológica

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |