Evaluation of a surgical technique for the treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis, retrospective phase
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29176/2590843X.244Keywords:
Axillary hyperhidrosis, treatment, surgeryAbstract
Objetive: To evaluate a surgical technique applied at the Clínica Universitaria Bolivariana and Clínica SOMA for the treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis.
Methodology: This is a two phase descriptive study: retrospective and prospective, with a month and one year follow-up.
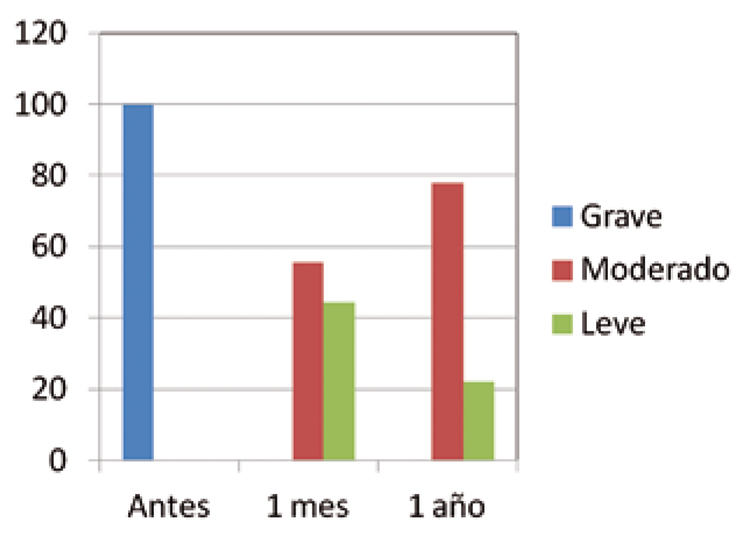
Results: Nine patients were admitted in the retrospective phase of the study, for a total of 18 surgical units. All patients had received previous treatment. The severity of the disease before surgery was high in all cases; one month after surgery, the severity was mild in four patientes and moderate in five; one year after surgery, the severity was mild in two patients and moderate in seven. Seven patients considered postoperative pain was mild and there was a low complication rate.
Conclusion: The proposed surgical technique for the management of axillary hyperhidrosis, is effective, has few complications and can be recommended as a second line therapy for patients that do not respond to conservative therapies.
Author Biographies
Claudia Andrea Hernández
Médica dermatóloga, Facultad de Medicina, Escuela de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia
Luz Marina Gómez
Médica dermatóloga; profesora titular; jefe, Servicio de Dermatología, Facultad de Medicina, Escuela de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Pontificia
Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia
Ángela Londoño
Médica dermatóloga y epidemióloga; docente, Facultad de Medicina, Escuela de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia
Natalia Mendoza
Médica, residente de III año de Dermatología, Facultad de Medicina, Escuela de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia.
References
2. Vorkamp T, Foo FJ, Khan S, Schmitto JD, Wilson P. Hyperhidrosis: Evolving concepts and a comprehensive review. Surgeon. 2010;8:287-92.
3. Schlereth T, Dieterich M, Birklein F. Hyperhidrosis-causes and treatment of enhanced sweating. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2009;106:32-7.
4. Togel B, Greve B, Raulin C. Current therapeutic strategies for hyperhidrosis: A review. Eur J Dermatol. 2002;12:219-23.
5. Strutton DR, Kowalski W, Glaswer DA, Stang PE: US prevalence of hyperhidrosis and impact on individuals with axillary hyperhidrosis: Results from a national survey. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004; 51:241-8.
6. Hurley HL, Shelley WB. Axillary hyperhidrosis clinical features and local surgical management. Br J Dermatol. 1966;78:127-41.
7. Hund M, Kinkelin I, Naumann M, Hamm H. Definition of axillary hyperhidrosis by gravimetric assessment. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:539-41.
8. Gómez F, Gómez LM. Hiperhidrosis axilar: un nuevo método de tratamiento y revisión de la literatura. Revista Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología. 1991;1:54-7.
9. Toro AM, Gómez LM. Curetaje subcutáneo en el manejo de la hiperhidrosis axilar. Revista Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología. 2007;237-40.
10. Hornberger J, Grimes K, Naumann M, Glaser DA, Lowe NJ, Naver H, et al. Recognition, diagnosis and treatment of primary focal hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:274-86.
11. Boni R. Generalized hyperhidrosis and its systemic treatment. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2002;30:44-7.
12. Flanagan KH, Glaser DA. An open-label trial of the efficacy of 15% aluminum chloride in 2% salicylic acid gel base in the treatment of moderate-to-severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2009;8:477-80.
13. Naumann MK, Hamm H, Lowe NJ. Effect of botulinum toxin type A on quality of life measures in patients with excessive axillary sweating: A randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:1218-26.
14. Naumann M, Lowe NJ, Kumar CJ, Hamm MD. Botulinum toxin type A is a safe and effective treatment for axillary hyperhidrosis over 16months: A prospective study. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:731-6.
15. Flanagan KH, King R, Glaser DA. Botulinum toxin type a versus topical 20% aluminum chloride for the treatment of moderate to severe primary focal axillary hyperhidrosis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:221-7.
16. Herbst F, Plas EG, Fugger R, Fritsch A. Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary hyperhidrosis of the upper limbs. A critical analysis and long-term results of 480 operations. Ann Surg. 1994;220:86-90.
17. Dumont P, Denoyer A, Robin P. Long-term results of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004;78:1801-7.
18. Swinehart JM. Treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis: combination of the starch-iodine test with the tumescent liposuction technique. Dermatol Surg. 2000;26:392-6.
19. Lee MR, Ryman WJ. Liposuction for axillary hyperhidrosis. Australas J Dermatol. 2005;46:76-9.
20. Jemec B. Abrasio axillae in hyperhidrosis. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1975;9:44-6.
21. Solish N, Bertucci V, Dansereau A, Hong HC, Lynde C, Lupin M, et al. A comprehensive approach to the recognition, diagnosis, and severity-based treatment of focal hyperhidrosis: Recommendations of the Canadian Hyperhidrosis Advisory Committee. Dermatol Surg. 2007:908:e23.
22. Lear W, Kessler E, Solish N, Glaser DA. An epidemiological study of hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Surg. 2007;33:S69-75.
23. Ou LF, Yan RS, Chen IC, Tang YW.Treatment of axillary bromhidrosis with superficial liposuction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998;102:1479- 85.
24. Jemec B, Holm Hansen B. Follow-up of patients operated on for axillary hyperhidrosis by subcutaneous curettage. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1978;12:65-7.
25. Darabaneanu S, Darabaneanu HA, Niederberger U, Russo PA, Lischner S, Hauschild A. Long-term efficacy of subcutaneous sweat gland suction curettage for axillary hyperhidrosis: A prospective gravimetrically controlled study. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:1170-7.
How to Cite
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section

| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |