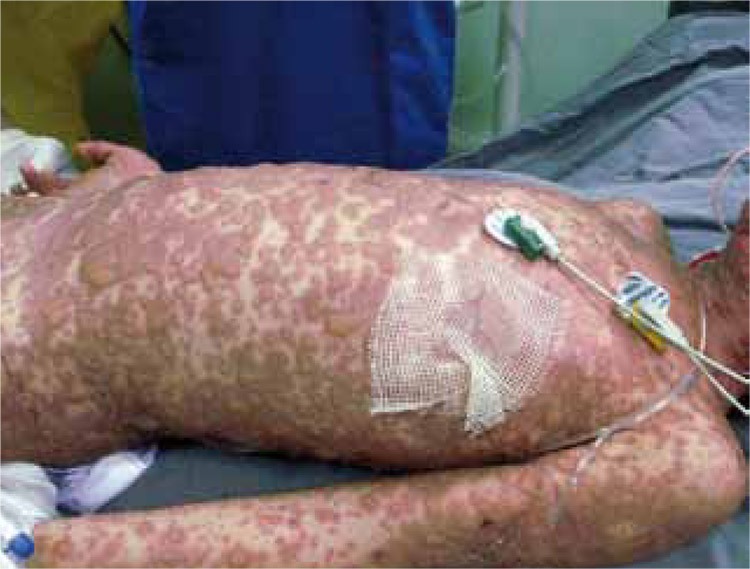
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis
Keywords:
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolisis, treatmentAbstract
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolisis are severe skin drug reactions that form part of the same entity. Despite its low frequency, they are associated with high morbidity and mortality rates. Although their physiopathology, classification and management are controversial, it is known that massive apoptosis of keratinocytes plays a role through different pathways. It should not be confused with erythema multiforme and there is not enough evidence to support the effectiveness of any treatment except support measures that are the mainstay of treatment. We present a literature revision of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolisis.
Author Biographies
Claudia Andrea Hernández
Residente Dermatología, Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia.
Rodrigo Restrepo
Dermatopatólogo y Docente Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia.
Milton Mejía
Dermatologo. Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia.
References
2. Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, Shear NH, Naldi L, Roujeau JC. Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129:92-6.
3. Stevens AM, Johnson FC. A new eruptive fever associated with stomatitis and ophthalmia. Am J Dis Child. 1922;¿Volumen?:526-32.
4. Lyell A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: An eruption resembling scalding of the skin. Br J Dermatol. 1956;68:355-61.
5. French LE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: Our current understanding. Allergology International. 2006;55:9-16.
6. Whorl S, Loewe R, Pickl WF, Stingl G, Wagner SN. EMPACT syndrome. Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2005;3:39-43.
7. Sharma VK, Sethuraman G, Minz A. Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and SJS-TEN overlap: A retrospective study of causative drugs and clinical outcome. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:238-40.
8. Mockenhaupt M, Kelly JP, Kaufman D, Stern RS; SCAR Study Group. The risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: A multinational perspective. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:2234-40.
9. Mockenhaupt M. Severe drug-induced skin reactions: Clinical pattern, diagnostics and therapy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2009;7:142-60.
10. Mockenhaupt M, Viboud C, Dunant A, Naldi L, Halevy S, Bouwes JN, et al. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: Assessment of medication risks with emphasis on recently marketed drugs. The EuroSCAR-Study. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:35-44.
11. Mockenhaupt M, Messenheimer J, Tennis P, Schlingmann J. Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in new users of antiepileptics. Neurology. 2005;64:1134-8.
12. Rzany B, Correia O, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Auquier A, Stern R. Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis during first weeks of antiepileptic therapy: A case control study. Lancet. 1999;353:2190.
13. Ball R, Ball LK, Wise RP, Braun MM, Beeler JA, Salive ME. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis after vaccination: Reports to the vaccine adverse event reporting system. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:219-23.
14. Chung WH, Hung SI, Hsih MS, Yang LC, Ho HC, Wu JY, et al. Medical genetics: A marker for Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Nature. 2004;428:486.
15. Yang CW, Hung SI, Juo CG, Lin YP, Fang WH, Lu IH, et al. HLA-B*1502-bound peptides: Implications for carbamazepine-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:870-7.
16. Laguna C, Martín B, Torrijos A, García-Melgares ML, Febrer I. Síndrome de Stevens-Johnson y necrólisis epidérmica tóxica: Experiencia clínica y revisión de la literatura especializada. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2006;97:177-85.
17. Viard I, Wehrli P, Bullani R, Schneider P, Holler N, Salomon D, et al. Inhibition of toxic epidermal necrolysis by blockade of CD95 with human intravenous immunoglobulin. Science. 1998;282:490-3.
18. Viard-Leveugle I, Bullani RR, Meda P, Micheau O, Limat A, Saurat JH, et al. Intracellular localization of keratinocyte Fas ligand explains lack of cytolytic activity under physiological conditions. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:16183-8.
19. Parrillo SP. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Current Allergy and Asthma Reports. 2007;7:243-7.
20. Bolognia JL, Jorizzo J, Rapini R. United States of America. Elsevier. Dermatology. 2nd edition. Madrid, España: Elsevier; 2008. p. 287-300.
21. Léauté-Labrèze C, Lamireau T, Chawki D, Maleville J, Taïeb A. Diagnosis, classification and management of erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 2000;83:347-52.
22. García-Doval I, LeCleach L, Bocquet H, Otero XL, Roujeau JC. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: Does early withdrawal of causative drugs decrease the risk of death? Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:323-7.
23. Magina S, Lisboa C, Leal V, Palmares J, Mesquita-Guimarães J. Dermatological and ophthalmological sequels in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Dermatology. 2003;207:33-6.
24. Roujeau JC, Stern RS. Severe cutaneous adverse reactions to drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:1272-85.
25. Wolkenstein P, Revuz J. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Dermatol Clin. 2000;18:485-95.
26. Crosi A, Borges S, Estévez F. Reacciones adversas medicamentosas graves: síndrome de Stevens-Johnson y necrólisis epidérmica tóxica. Rev Med Uruguay. 2004;20:172-7.
27. Vanfleteren I, VanGysel D, DeBrandt C. Stevens-Johnson syndrome: A diagnostic challenge in the absence of skin lesions. Ped Dermatol. 2003;20:152-6.
28. Sheridan RL, Liu V, Anupindi S. Case 34-2005: A 10-year-old girl with a bullous skin eruption and acute respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2057-66.
29. Quinn AM, Brown K, Bonish BK, Curry J, Gordon KB, Sinacore J, et al. Uncovering histologic criteria with prognostic significance in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:683-7.
30. Ringheanu M, Laude TA. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in children: An update. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2000;39:687-94.
31. Bastuji-Garin S, Fouchard N, Bertocchi M, Roujeau JC, Revuz J, Wolkenstein P. SCORTEN: A severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:149-53.
32. Vaishampayan S, Das A, Verma R. SCORTEN: Does it need modification? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:35-7.
33. Sheridan RL, Weber JM, Schulz JT, Ryan CM, Low HM, Tompkins RG. Management of severe Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in children. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:497-500.
34. Schulz JT, Sheridan RL, Ryan CM, MacKool B, Tompkins RG. A 10-year experience with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2000;21:199-204.
35. Fromowitz J, Ramos-Caro F, Flowers F. Practical guidelines for the management of toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:1092-4.
36. Chave TA, Mortimer NJ, Sladden MJ, Hall AP, Hutchinson PE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: Current evidence, practical management and future directions. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153:241-53. 3
7. Pirrung MK. Management of toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Intraven Nurs. 2001; 24:10712.
38. Arevalo JM, Lorente JA. Skin coverage with Biobrane biomaterial for the treatment of patients with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:406-10.
39. van der Meer JB, Schuttelaar ML, Toth GG, Kardaun SH, Beerthuizen G, de Jong MC, et al. Successful dexamethasone pulse therapy in a toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) patient featuring recurrent TEN to oxazepam. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001;26:654.
40. Tripathi A, Ditto AM, Grammer LC, Greenberger PA, McGrath KG, Zeiss CR, et al. Corticosteroid therapy in an additional 13 cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome: A total series of 67 cases. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2000;21:101-5.
41. Enk A, European Dermatology Forum Guideline Subcommittee. Guidelines on the use of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in dermatology. Eur J Dermatol. 2009;19:90-8.
42. Prins C, Kerdel FA, Padilla RS, Hunziker T, Chimenti S, Viard I, et al. Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins: Multicenter retrospective analysis of 48 consecutive cases. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:26-32.
43. Metry D, Jung P, Levy ML. Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in children with SJS and TEN: Seven cases and review of the literature. Pediatrics. 2003;112:1430-6.
44. Schneck J, Fagot JP, Sekula P, Sassolas B, Roujeau JC, Mockenhaupt M. Effects of treatments on the mortality of Stevens-Johnsons syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: A retrospective study on patients included in the prospective EuroSCAR Study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:33-40.
45. Arevalo JM, Lorente JA, González-Herrada C, Jiménez-Reyes J. Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with cyclosporin A. J Trauma. 2000;48:473-8.
46. Furubacke A, Berlin G, Anderson C, Sjöberg F. Lack of significant treatment effect of plasma exchange in the treatment of drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis? Intensive Care Med. 1999;25:1307-10.
How to Cite
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |