Langerhan cells in cutaneous inmunity.
Keywords:
Langerhans cells, antigen presentation, epidermis, naïve T cellsAbstract
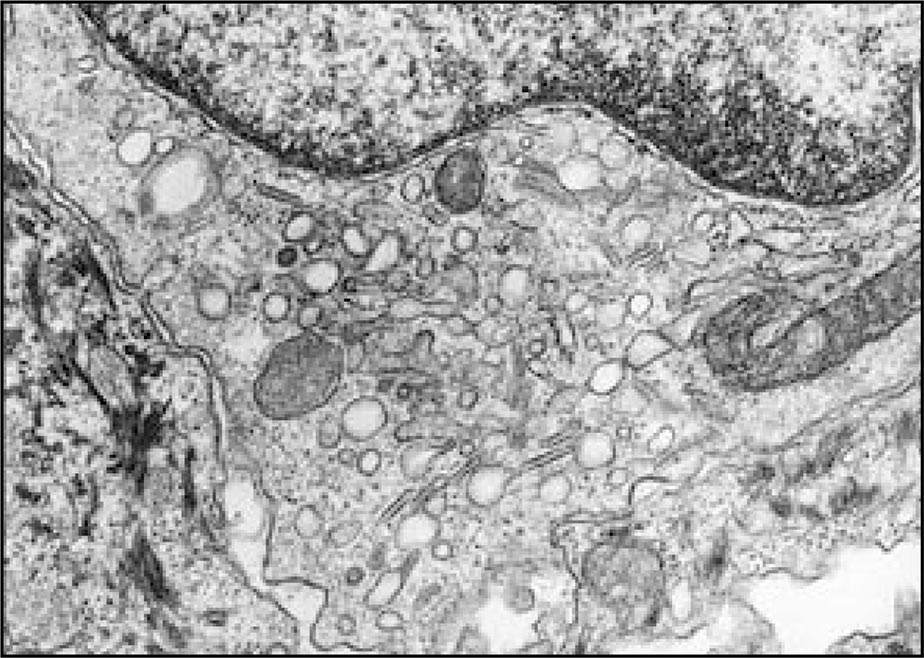
Langerhans cells (LC) have hematopoietic origin, and they belong to the family of antigen-presenting cells. They are in the epidermis and they are discussed to be crucial for antigen uptake and its subsequent presentation to naive T cells in skin-draining lymph nodes. The density and morphology of epidermal LCs are altered under normal and pathological conditions in the skin.
Author Biography
Diego Mauricio Ordóñez
Residente II año Dermatología, Universidad del Valle.
References
2. Stingl G, Maurer D, Wolff K. The epidermis : an immunologic microenviroment. In : Freedberg I, Eisen A, Wolff K, Austen F, Goldmith L, Katz S, eds. Fitzpatricks in General Medicine, 6 ed. 2003:343-57.
3. Bucana CD, Munn CG, Song MJ, Dunner K, Kripke ML. Internalization of the molecules into Birbeck granule-like structures in murine dendritic cells. J Invest Dermatol 1992; 99: 365-73.
4. Abbas AK, Lichtman AH. Cellular and Molecular Inmunology fifth ed.2003:32-3.
5. Cohen P, Katz S. Culture human Langerhans cels process and present intact proteine antigens. J. Invest Dermatol. 1992; 99:331-6.
6. Setum CM, Serie JR, Hegre OP, Dendritic cell/lymphocyte clustering: morphologic analysis by transmission electron microscopy and distribution of gold-labeled MHC class antigens by high-resolution scanning electron microscopy. Anat Rec. 1993; 235: 285-95.
7. Saeki H, Tamaki K. Thymus and activation regulated chemokine (TARC)/CCL17 and skin diseases.J Dermatol Sci. 2006; 43: 75-84.
8. Guess JC, McCance DJ. Decreased migration of Langerhans precursor-like cells in response to human keratinocytes expressing human papillomavirus type 16 E6/E7 is related to reduced macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha production. J Virol. 2005 ;79:14852-62.
9. M.Gombert. M.Dieu-Nosjean.CCL1-CCR8 Interactions: An Axis Mediating the Recruitment of T Cells and LangerhansType Dendritic Cells to Sites of Atopic Skin Inflammation. The Journal of Immunology, 2005, 174: 5082-91.
10. McKenna K, Beignosn AS. Plasmocytoid Dendritic Cells : linking innate and adaptive inmunity Journal of Virology.Jan 2005. 79 ; 1:17-27.
11. Rademakers LH. Dark and light zones of germinal centres of the human tonsil: an ultrastructural study with emphasis on heterogeneity of follicular dendritic cells. Cell-Tissue-Res 1992; 269: 359-68.
12. Bacci S, Nakamura T, Streilein JW. Failed Antigen Presentation After UVB Radiation Correlates With Modifications of Langerhans Cell Cytoskeleton. Journal of Investigative Dermatology.1996; 107: 838–43.
13. Braun L, Durst M, Mikumo R, Crowley A, Robinson M. Regulation of growth in human papillomavirus-transformed keratinocytes by transforming growth factor-ß: Implications for the control of papillomavirus infection. Mol Carcinog 1992;6:100-11.
14. Ghosh AK , Moore M. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in cervical carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 1992;11:1910-16.
15. Stoitzner P, Pfaller K, Stössel H, Romani N. A close-up view of migrating langerhans cells in the skin. J Invest Dermatol 2002, 118:117-25.
16. Shortman K, Liu YJ. Mouse and human dendritic cell subtypes. Nat Rev Immunol 2002;2:151-61.
17. Klinkert ME. Lymphoid dendritic accesory cells of the rat, Immunol Rev 1990; 117: 103-20.
18. Cumberbatch M, Singh M, Dearman RJ, Young HS, Kimber I, Griffiths CE. Impaired Langerhans cell migration in psoriasis. J Exp Med. 2006 Apr 17;203: 953-60.
19. Delgado V. Mori R. Células de Langerhans en Piel de Pacientes con Síndrome de Inmunodeficiencia Adquirida. Folia Dermatológica Peruana . 1995; 6: 25.
20. Leyva ER, Vega E. Identificación y distribución de celulas de langerhans en liquen plano y penfigo vulgar. Revista Mexicana de Patología Clinica. 2004; 51: 42-8.
21. Kao CH. Yu HS. Depletion and repopulation of Langerhans cells in nonsegmental type vitiligo.J Dermatol 1990 May; 17:287-96.
22. Caux C, Dezutter-Dambuyant C, Schmitt D, Banchereau J. GM-CSF and TNF-α cooperate in the generation of dendritic langerhans cells. Nature 1992;360:258-61.
23. Reid CD, Stackpoole A, Meager A, Tikerpae J. Interactions of tumor necrosis factor with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines in the regulation of dendritic cell growth in vitro from early bipotent CD34 + progenitors in human bone marrow. J Immunol 1992;149:2681-8.
24. Santiago-Schwarz F, Belilos E, Diamond B, Carsons SE. TNF in combination with GM-CSF enhances the differentiation of neonatal cord blood stem cells into dendritic cells and macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 1992;52:274-81.
25. Santiago-Schwarz F, Divaris N, Kay C, Carsons SE. Mechanisms of tumor necrosis factor-granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-induced dendritic cell development. Blood 1993;82:3019-28.
26. Santamaría LF. Las celulas de Langerhans en la inmunidad cutanea con especial referencia a la dermatitis atopica. Actualidad dermatológica.1998;3:173-81.
27. Pulendran B, van Driel R, Nossal G. Immunological tolerance in germinal centres. Immunol Today 1997; 18: 27-31.
28. Gilliet M, Liu YJ. Human plasmacytoid-derived dendritic cells and the induction of T-regulatory cells. Hum Immunol 2002;63:1149-55.
29. Kleijmeer MJ, Ossevoort MA, van Veen CJ, van-Hellemond JJ, Neefjes JJ, Kast WM et al. MHC class II compartments and the kinetics of antigen presentation in activated mouse spleen dendritic cells. J Immunol 1995; 154: 5715-24.
30. Guery JC, Adorini L. Dendritic cells are the most efficient in presenting endogenous naturally processed self-epitopes to clase II- restrictes T cells. J Immunol 1995; 154: 536-44.
31. Stift A, Friedl J, Dubsky P, Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Schueller G, Zontsich T, et al. Dendritic cell-based vaccination in solid cancer. J Clin Oncol 2003;21:135-42.
32. Tatsumi T, Storkus WJ. Dendritic cell-based vaccines and therapies for cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2002;2:919-28.
33. Berumen J. Villegas N. Vacunas terapéuticas recombinantes contra el cáncer del cuello uterino..Salud Publica Mex 1997;39:288-97.
How to Cite
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |