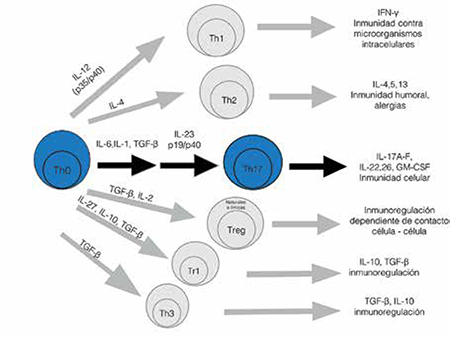
Immunopathogenic aspects of IL-17 in psoriasis: a novel therapeutic target
Keywords:
IL-17, Psoriasis, immunopathogenesis, cytokines.Abstract
Psoriasis is a multifactorial, common disease in which environmental, immunological and genetic factors are involved. Its immunopathogenesis is mediated by multiple cytokines that have turned into a therapeutic target. IL-17 is necessary in the immunity against intracellular and extracellular pathogens, but can also contribute in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, mediating inflammation and recruiting cells. There are ongoing trials with drugs that block this cytokine and its receptor, with promising results.
Author Biographies
Luis Carlos Ramírez
Médico, residente de segundo año de Dermatología, Sección de Dermatología, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia
Médico, residente de segundo año de Dermatología, Sección de Dermatología, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia Velásquez
Médica dermatóloga, doctora en Ciencias Básicas Biomédicas con énfasis en Inmunología; profesora, Sección de Dermatología, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia, Centro de Investigaciones Dermatológicas, CIDERM, Medellín, Colombia.
References
2. Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:496-509.
3. González C, Castro L, Londoño A, Vargas A, Velásquez M. Psoriasis: aspectos epidemiológicos, inmunológicos, clínicos y terapéuticos. En: Olmos E, editor. Texto de dermatología. Segunda edición. Bogotá: Servicio de Dermatología, Hospital San José; 2013. p. 655-73.
4. Gudjonsson J, Elder J. Psoriasis. In: Wolff K, Goldsmith L, Katz S, Gilchrest B, Paller A, Leffell D. Fitzpatrick’s dermatology in general medicine. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2007. p. 169-93.
5. Horn EJ, Fox KM, Patel V, Chiou C-F, Dann F, Lebwohl M. Association of patient-reported psoriasis severity with income and employment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:963-71.
6. Sabat R, Philipp S, Höflich C, Kreutzer S, Wallace E, Asadullah K, et al Immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. Exp Dermatol. 2007;16:779-98.
7. Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007;370:263-71.
8. Wu JJ, Nguyen TU, Poon K-YT, Herrinton LJ. The association of psoriasis with autoimmune diseases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:924-30.
9. Londoño A, González C, Castro L. Psoriasis y su relación con el síndrome metabólico. Rev Colomb Reumatol. 2013;20:228-36.
10. González S, Queiro R, Ballina J. Actualización en la patogenia de la artritis psoriásica. Reumatol Clín. 2012;8:1-6.
11. Chandran V, Raychaudhuri SP. Geoepidemiology and environmental factors of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2010;34:J314-21.
12. Chandran V. The genetics of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012;44:149-56.
13. Bowcock AM, Krueger JG. Getting under the skin: The immunogenetics of psoriasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:699-711.
14. Rahman P, Elder JT. Genetic epidemiology of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(Suppl.2):ii37-9.
15. Asumalahti K, Laitinen T, Itkonen-Vatjus R, Lokki M-L, Suomela S, Snellman E, et al. A candidate gene for psoriasis near HLA-C, HCR (Pg8), is highly polymorphic with a disease-associated susceptibility allele. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:1533-42.
16. Nair RP, Duffin KC, Helms C, Ding J, Stuart PE, Goldgar D, et al. Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-κB pathways. Nat Genet. 2009;41:199-204.
17. Schön MP, Boehncke W-H. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1899-912.
18. Newman MD, Weinberg JM. The pathophysiology of psoriasis. Milestones in drug therapy: Treatment of psoriasis. New York: Springer; 2008. p. 11-21.
19. Nickoloff BJ, Qin J-Z, Nestle FO. Immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2007;33:45-56.
20. Ghoreschi K, Weigert C, Röcken M. Immunopathogenesis and role of T cells in psoriasis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:574-80.
21. Girolomoni G, Mrowietz U, Paul C. Psoriasis: Rationale for targeting interleukin-17: IL-17 in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:717-24.
22. Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P, Nestle FO. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:1339-50.
23. van Beelen AJ, Teunissen MB, Kapsenberg ML, de Jong EC. Interleukin-17 in inflammatory skin disorders. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;7:374-81.
24. Gaffen SL. Recent advances in the IL-17 cytokine family. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011;23:613-9.
25. Raychaudhuri SP. Role of IL-17 in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013;44:183-93.
26. Stockinger B, Veldhoen M, Martin B. Th17 T cells: Linking innate and adaptive immunity. Semin Immunol. 2007;19:353-61.
27. Teunissen MBM, Koomen CW, de Waal Malefyt R, Wierenga EA, Bos JD. Interleukin-17 and interferon-γ synergize in the enhancement of proinflammatory cytokine production by human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1998;111:645-9.
28. Lowes MA, Kikuchi T, Fuentes-Duculan J, Cardinale I, Zaba LC, Haider AS, et al. Psoriasis vulgaris lesions contain discrete populations of Th1 and Th17 T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:1207-11.
29. Miossec P. IL-17 and Th17 cells in human inflammatory diseases. Microbes Infect. 2009;11:625-30.
30. Pappu R, Ramírez-Carrozzi V, Sambandam A. The interleukin-17 cytokine family: Critical players in host defence and inflammatory diseases: IL-17 cytokine family. Immunology. 2011;134:8-16.
31. Lin AM, Rubin CJ, Khandpur R, Wang JY, Riblett M, Yalavarthi S, et al. Mast cells and neutrophils release IL-17 through extracellular trap formation in psoriasis. J Immunol. 2011;187:490-500.
32. Becher B, Pantelyushin S. Hiding under the skin: Interleukin-17-producing γδ T cells go under the skin? Nat Med. 2012;18:1748-50.
33. Flores-García Y, Talamás-Rohana P. Interleucina 17, funciones biológicas y su receptor. REB Revista de Educación Bioquímica. 2012;31:3-9.
34. Gu C, Wu L, Li X. IL-17 family: Cytokines, receptors and signaling. Cytokine. 2013;64:477-85.
35. Martin DA, Towne JE, Kricorian G, Klekotka P, Gudjonsson JE, Krueger JG, et al. The emerging role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: Preclinical and clinical findings. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;133:17-26.
36. Pappu R, Ramírez-Carrozzi V, Ota N, Ouyang W, Hu Y. The IL-17 family cytokines in immunity and disease. J Clin Immunol. 2010;30:185-95.
37. Gaffen SL. Structure and signalling in the IL-17 receptor family. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:556-67.
38. Nograles KE, Zaba LC, Guttman-Yassky E, Fuentes-Duculan J, Suárez-Fariñas M, Cardinale I, et al. Th17 cytokines interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-22 modulate distinct inflammatory and keratinocyte-response pathways. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:1092–102.
39. Nograles KE, Davidovici B, Krueger JG. New insights in the immunologic basis of psoriasis. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:3-9.
40. Krueger JG, Fretzin S, Suárez-Fariñas M, Haslett PA, Phipps KM, Cameron GS, et al. IL-17A is essential for cell activation and inflammatory gene circuits in subjects with psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:145-54.
41. van der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JS, Kant M, Boon L, Laman JD, et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J Immunol. 2009;182:5836-45.
42. Chiricozzi A, Guttman-Yassky E, Suárez-Fariñas M, Nograles KE, Tian S, Cardinale I, et al. Integrative responses to IL-17 and TNF-α in human keratinocytes account for key inflammatory pathogenic circuits in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:677-87.
43. Kupetsky EA, Mathers AR, Ferris LK. Anti-cytokine therapy in the treatment of psoriasis. Cytokine. 2013;61:704-12.
44. Crow JM. Therapeutics: Silencing psoriasis. Nature. 2012;492:S58-9.
45. Zaba LC, Suárez-Fariñas M, Fuentes-Duculan J, Nograles KE, Guttman-Yassky E, Cardinale I, et al. Effective treatment of psoriasis with etanercept is linked to suppression of IL-17 signaling, not immediate response TNF genes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1022-30.
46. Antiga E, Volpi W, Cardilicchia E, Maggi L, Filì L, Manuelli C, et al. Etanercept downregulates the Th17 pathway and decreases the IL-17+/IL-10+ cell ratio in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Clin Immunol. 2012;32:1221-32.
47. Ryan C, Leonardi CL, Krueger JG, Kimball AB, Strober BE, Gordon KB, et al. Association between biologic therapies for chronic plaque psoriasis and cardiovascular events: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA. 2011;306:864-71.
48. Puel A, Cypowyj S, Bustamante J, Wright JF, Liu L, Lim HK, et al. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in humans with inborn errors of interleukin-17 immunity. Science. 2011;332:65-8.
49. Leonardi C, Matheson R, Zachariae C, Cameron G, Li L, Edson-Heredia E, et al. Anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody ixekizumab in chronic plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1190-9.
50. Gordon KB, Leonardi CL, Lebwohl M, Blauvelt A, Cameron GS, Braun D, et al. A 52-week, open-label study of the efficacy and safety of ixekizumab, an anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:1176-82.
51. Papp KA, Langley RG, Sigurgeirsson B, Abe M, Baker DR, Konno P, et al. Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II dose-ranging study. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:412–21.
52. Paul C, Lacour JP, Tedremets L, Kreutzer K, Jazayeri S, Adams S, et al. Efficacy, safety and usability of secukinumab administration by autoinjector/pen in psoriasis: A randomized, controlled trial (JUNCTURE); the JUNCTURE study group. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2014;22: doi: 10.1111/jdv.12751.
53. Langley RG, Elewski BE, Lebwohl M, Reich M, Griffiths CEM. Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis -results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:326-38.
54. Papp KA, Leonardi C, Menter A, Ortonne J-P, Krueger JG, Kricorian G, et al. Brodalumab, an anti–interleukin-17–receptor antibody for psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1181-9.
55. Papp K, Leonardi C, Menter A, Thompson EHZ, Milmont CE, Kricorian G, et al. Safety and efficacy of brodalumab for psoriasis after 120 weeks of treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:1183-90.
56. Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, Pillai S. Inmunologia celular y molecular. Philadelphia: Elsevier. 2011. p. 214-9.
57. Miossec P, Korn T, Kuchroo VK. Interleukin-17 and type 17 helper T cells. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:888-98.
58. González C, Londoño A, Castro L. Asociación Colombiana de Dermatología y Cirugía Dermatológica Asocolderma, Grupo Colombiano de Psoriasis Colpsor. Guías basadas en la evidencia para el manejo de la psoriasis en Colombia. Bogotá: Editorial Panamericana; 2012
59. Giraldo C, Velásquez MM. Psoriasis: A review with emphasis on immunopathogenesis. Iatreia. 2009;22:272-83.
How to Cite
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |