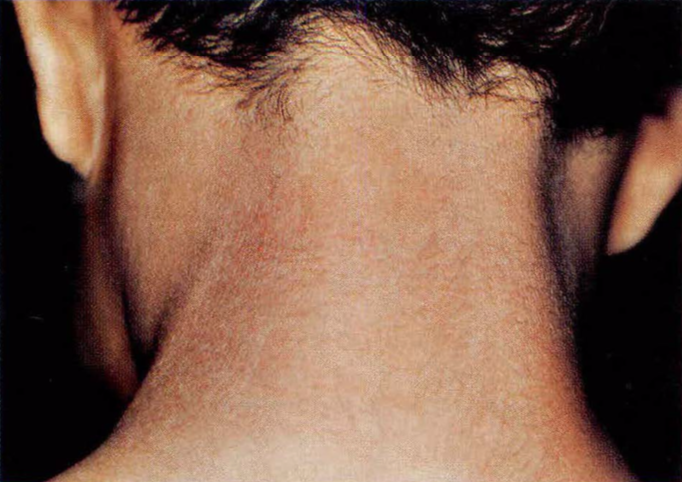
Conceptos básicos, clínicos y terapéuticos de la dermatitis atópica
Palabras clave:
dermatitis atópica, alergia, genética, fisiopatología, tratamientoResumen
La dermatitis atópica (DA) es una enfermedad inflamatoria crónica de la piel, que con frecuencia antecede a la aparición de la rinitis alérgica y el asma. Esta enfermedad genera una alta morbilidad y costos significativos para su atención, puesto que puede afectar hasta el 20% de los niños; se ha observado un aumento en su prevalencia en las dos últimas décadas. Estudios recientes han demostrado la compleja interrelación de factores genéticos, ambientales, farmacológicos e inmunológicos que contribuyen al desarrollo y severidad de la DA. En esta revisión se examinan los mecanismos celulares, moleculares e inmunológicos involucrados en la patogénesis de la DA, así como las diferentes posibilidades terapéuticas para esta enfermedad.
Biografía del autor/a
Liliana María Tamayo Quijano, Universidad de Antioquia
Dermatóloga, Profesora Unidad de Alergias, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia.
Carlos Julio Montoya Guarín, Universidad de Antioquia
Profesor Centro de Investigaciones Médicas, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia.
Helí Salgado Vélez, Universidad de Antioquia
Pediatra, lnmunólogo, Profesor Departamento de Microbiología y Parasitología,. Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia.
Ricardo Cardona Villa, Universidad de Antioquia
Alergólogo, Profesor Unidad de Alergias, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad de Antioquia.
Referencias bibliográficas
Leung DYM, Boguniewics M. Atopic dermatitis. En: Austen KF, Frank MM, Atkinson JP, et al. Samter's l mmunologic Diseases. Fidadelfia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins 2001:877-889.
Beltrani VS. The clinical spectrum of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 1999; 104:S87-98.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(99)70050-3
Boguniewicz M, Leung DYM. Atopic dermatitis. En: Middleton E. Allergy. Principies and Practice 2000: 1123-1134.
Leung DYM. Atopic dermatitis: new insights and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 2000; 105:860-876.
https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2000.106484
LeungDYM. Allergic and immunologic skin disorders. JAMA 1997; 278:1914-1923.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1997.03550220120016
Nicol NH. Managing atopic dermatitis in children and adults. The Nurse Practitioner 2000; 25:59-69.
https://doi.org/10.1097/00006205-200025040-00004
Williams HC. Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis. En: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N. Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology, Oxford, Blackwell Science 2000:161- 168.
Kristal L, Klein PA. Atopic dermatitis in infants and children. Pediatr Clin North Am 2000; 47:877-895.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3955(05)70246-7
Hanifin J, Chan S. Diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis. Dermatologic Therapy 1996; 1:9-18.
https://doi.org/10.3109/09546639609097188
Cox H, Cookson WOM, Harper J. Genetics of atopic dermatitis. En: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N. Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology, Oxford, Blackwell Science 2000: 169-177.
Archer CB. Pharmacological mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. En: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N. Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology, Oxford, Blackwell Science; 2000: 186-193.
Bos JD. lmmunology of atopic dermatitis. En: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N. Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology, Oxford, Blackwell Science 2000:178-185.
Leung DYM. Pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 1999; 104:S99-108.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(99)70051-5
Sicherer SH, Sampson HA. Food hypersensitivity and atopic dermatitis: pathophysiology, epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 1999; 104:S114-122.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(99)70053-9
David TJ, Patel L, Ewing TI, et al. The role of diet in atopic dermatitis. En: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N. TextbookofPediatricDermatology,Oxford, Blackwell Science 2000:231-236.
Leung DYM. Atopic dermatitis: the skin as a window into the pathogenesis of chronic allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 1995; 96:302-318.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(95)70049-8
Borkowski T, Sampsom HA. A combined dermatology and allergy approach to the management of suspected food allergy. Dermatologic Therapy 1996; 1:38-50.
Sampson HA, Sicherer SH. Eczema and food hypersensitivity. lmmunol Allergy Clin North Am 1999; 19:495-517.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0889-8561(05)70104-1
Ring J, Darsow U, Abeck D. The atopy patch test as a method of studying aeroallergens as triggering factors of atopic eczema. Dermatologic Therapy 1996;1:51-60.
Charlesworth EN. Atopic eczema and the allergist. Allergy Asthma Proc 1999; 20:305-310.
https://doi.org/10.2500/108854199778251933
Nakagawa S, Aiba S, Tagami H. Decreased frequency of interferon-y-producing CD4+ cells in the peripheral blood of patients with atopic dermatitis. Exp Dermatol 1998; 7:112-118.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.1998.tb00310.x
Nakazawa M, Sugi N, Kawaguchi H, et al. Predo minance of type 2 cytokine-producing CD4+ and CDS+ cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 1997; 99:673-682.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(97)70030-7
Kimura M, Tsuruta S, Yoshida T. Unique profile of IL- 4 and IFN-y production by peripheral blood mono nuclear cells in infants with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 1998; 102:238-244.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(98)70092-2
Parnia S. Chemokines and atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 2000; 105:892-894.
https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2000.106570
Poulsen LK. Differential lgE regulation in atopic dermatitis and inhalant allergy. Allergy Clin lmmunol lntern 1998;10:12-15.
Sosa M, Orea M, Florez G. Nuevos conceptos en dermatitis atópica. Revista Alergia México 2001; 48:15-24.
Leung DYM. Atopic dermatitis: immunobiology and treatment with immune modulators. Clin Exp lnmunol 1997; 107:25-30.
Hebert A, Mays S. Atopic dermatitis of infancy. Dermatol Ther 1996;1:61-64.
Klobenzer CS. ltching and the atopic skin. J Allergy Clin lmmunol 1999; 104:S109-113.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(99)70052-7
Kunz B, Ring J. Clinical features and diagnostic criteria of atopic dermatitis. En: Harper J, Oranje A, ProseN. TextbookofPediatricDermatology,Oxford, Blackwell Science 2000:199-214.
Vásquez LA. Dermatitis Atópica. Medicina UPB 2002; 19:59-72.
Lever R. lnfection in atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther 1996; 1:32-37.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0163-4453(96)91932-5
Harrigan E, Rabinowitz LG. Atopic dermatitis. lmmunol Allergy Clin NA 1999; 19:383-396.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0889-8561(05)70094-1
Lever R. Microbiology of atopic dermatitis. En: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N. Textbook of Pediatric Derma tology, Oxford, Blackwell Science 2000:194-198.
Goodyear H. Eczema herpeticum. En: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N. Textbook of Pediatric Derma tology, Oxford, Blackwell Science 2000:242-246.
Uehara M, Omoto M, Sugiura H. Diagnosis and management of the red face syndrome. Dermatologic Therapy 1996; 1:19-23.
Warner JO. Environmental allergens in atopic derma titis. En: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N. Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology, Oxford, Blackwell Science 2000:238-241.
Bohme M, Svensson A, Kull 1, et al. Hanifin's and Rajka's minor criteria for atopic dermatitis: Which do 2-year-old exhibit? J Am Acad Dermatol 2000; 43:785-790.
https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2000.110070
Nicol NH. Atopic dermatitis: the itch continues. En: Atopic Dermatitis; New Orleans: 57th AAA Annual Meeting 2001.
Ringel M. Un enfoque práctico para tratar las derma titis. Patient Care 1999:14-27.
Cerio R. Therapy of atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 1997; 8:S6-1O.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.1997.tb01068.x
Bingham EA. Guidelines to management of atopic dermatitis. En: Harper J, Oranje A, Prose N. Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology, Oxford, Blackwell Science 2000:215-230.
Bigby M. A thorough systematic review of treatment for atopic eczema. Arch Dermatol 2001; 137:1635-1636.
https://doi.org/10.1001/archderm.137.12.1635
Williams REA. The antibacterial-corticosteroid combination: what is its role in atopic dermatitis? Am J Clin Dermatol 2000; 1:211-215.
https://doi.org/10.2165/00128071-200001040-00002
Lane AT. Efficacy and safety of topical steroids in paediatric atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 1997; 8:S24-27.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-9959(97)90020-9
Abeck D, Strom K. Optima! management of atopic dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol 2000; 1:41-46.
https://doi.org/10.2165/00128071-200001010-00004
Drake LA, Fallon JO, SoberA. Relief of pruritus in patients with atopic dermatitis after treatment with topical doxepin cream. J Am Acad Dermatol 1994; 31:613-616.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(94)70225-X
Tang WYM, Chan HHL, Lam VMF, et al. Outpatient, short term, once daily, diluted, 0.1 % mometasone furoate wet wraps for childhood atopic eczema. J Dermatol Treatm 1999; 10:157-163.
https://doi.org/10.3109/09546639909056022
KrutmannJ,DiepgenTL,LugerTA,etal.High-dose UVA1 therapy for atopic dermatitis: results of a multicenter trial. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998; 38:589-593.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(98)70123-9
Krutmann J. Phototherapy for atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther 1996; 1:24-31.
Richter HI, Billmann-Eberwein P, Grewe M, et al. Successful monotherapy of severe and intractable atopic dermatitis by photopheresis. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998; 38:585-588.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(98)70122-7
Nghien P. lmmunomodulators: introducing old friends. JAmAcad Dermatol 2001; 44:111-113.
https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2001.110902
Fleischer A. Treatment of atopic dermatitis: role of tacrolimus ointment as a topical noncorticosteroidal therapy. JAllergy Clin lmmunol 1999; 104:S126-130.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-6749(99)70055-2
Raewyn P. Pimecrolimus: an effective long-term therapy for atopic dermatitis. lnpharma Weekly 2002; 1329:15-17.
https://doi.org/10.2165/00128413-200213290-00033
RanaweeraA. Pimecrolimus long-term management of inflammatory skin diseases. lnpharma Weekly 2001;1281:11-12.
https://doi.org/10.2165/00128413-200112810-00021
Wellington K, Blair J. Topical pimecrolimus: a review of its clinical potential in the management of atopic dermatitis. Drugs 2002; 62:817-840.
https://doi.org/10.2165/00003495-200262050-00007
Jolles S, Hughes J, Rustin M. The treatment of atopic dermatitis with adjunctive high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin: a report of three patients and review of the literature. Br J Dermatol 2002; 142:551-554.
https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03377.x
Wedi 8, KappA. Pathophysiological role of leuko- trienes in dermatological diseases: potential thera- peutic implications. BioDrugs 2001; 15:729-743.
https://doi.org/10.2165/00063030-200115110-00004
Rustin M, Poulter L. Chinese herbal therapy in atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther 1996; 1:83-93.
Cómo citar
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |