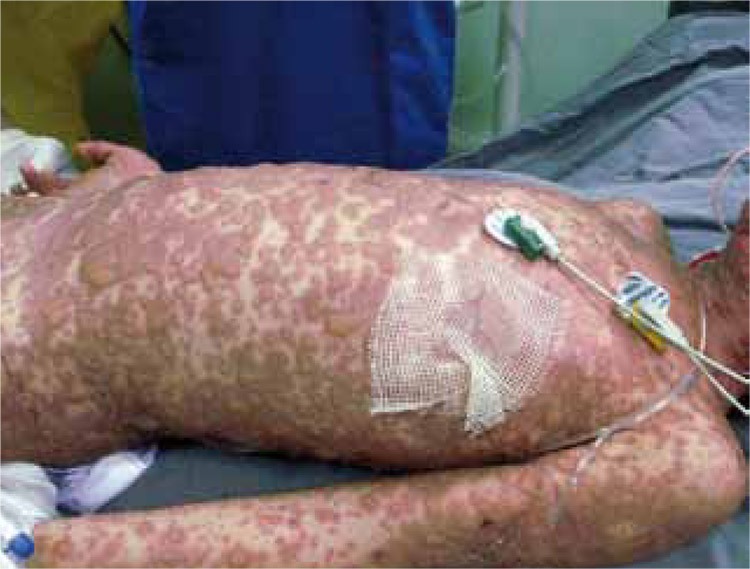
Síndrome de Stevens-Johnson y necrólisis epidérmica tóxica
Palabras clave:
síndrome de Stevens-Johnson, necrólisis epidérmica tóxica, tratamientoResumen
El síndrome de Stevens-Johnson y la necrólisis epidérmica tóxica son toxicodermias graves que forman parte de un mismo espectro de enfermedad y que, pese a su baja frecuencia, se asocian con una gran morbimortalidad. Aunque su fisiopatología, clasificación y manejo son controvertidos, se sabe que la apoptosis masiva de queratinocitos por diferentes vías se encuentra implicada. No deben confundirse con el eritema multiforme y hasta el momento no se ha demostrado la seguridad y eficacia de los tratamientos, excepto de las medidas de soporte que son el pilar del manejo. A continuación se presenta una revisión de la literatura sobre el síndrome de Stevens-Johnson y la necrólisis epidérmica tóxica.
Biografía del autor/a
Claudia Andrea Hernández
Residente Dermatología, Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia.
Rodrigo Restrepo
Dermatopatólogo y Docente Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia.
Milton Mejía
Dermatologo. Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana, Medellín, Colombia.
Referencias bibliográficas
2. Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, Shear NH, Naldi L, Roujeau JC. Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Arch Dermatol. 1993;129:92-6.
3. Stevens AM, Johnson FC. A new eruptive fever associated with stomatitis and ophthalmia. Am J Dis Child. 1922;¿Volumen?:526-32.
4. Lyell A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: An eruption resembling scalding of the skin. Br J Dermatol. 1956;68:355-61.
5. French LE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: Our current understanding. Allergology International. 2006;55:9-16.
6. Whorl S, Loewe R, Pickl WF, Stingl G, Wagner SN. EMPACT syndrome. Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2005;3:39-43.
7. Sharma VK, Sethuraman G, Minz A. Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and SJS-TEN overlap: A retrospective study of causative drugs and clinical outcome. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:238-40.
8. Mockenhaupt M, Kelly JP, Kaufman D, Stern RS; SCAR Study Group. The risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs: A multinational perspective. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:2234-40.
9. Mockenhaupt M. Severe drug-induced skin reactions: Clinical pattern, diagnostics and therapy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2009;7:142-60.
10. Mockenhaupt M, Viboud C, Dunant A, Naldi L, Halevy S, Bouwes JN, et al. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: Assessment of medication risks with emphasis on recently marketed drugs. The EuroSCAR-Study. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:35-44.
11. Mockenhaupt M, Messenheimer J, Tennis P, Schlingmann J. Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in new users of antiepileptics. Neurology. 2005;64:1134-8.
12. Rzany B, Correia O, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Auquier A, Stern R. Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis during first weeks of antiepileptic therapy: A case control study. Lancet. 1999;353:2190.
13. Ball R, Ball LK, Wise RP, Braun MM, Beeler JA, Salive ME. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis after vaccination: Reports to the vaccine adverse event reporting system. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:219-23.
14. Chung WH, Hung SI, Hsih MS, Yang LC, Ho HC, Wu JY, et al. Medical genetics: A marker for Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Nature. 2004;428:486.
15. Yang CW, Hung SI, Juo CG, Lin YP, Fang WH, Lu IH, et al. HLA-B*1502-bound peptides: Implications for carbamazepine-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:870-7.
16. Laguna C, Martín B, Torrijos A, García-Melgares ML, Febrer I. Síndrome de Stevens-Johnson y necrólisis epidérmica tóxica: Experiencia clínica y revisión de la literatura especializada. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2006;97:177-85.
17. Viard I, Wehrli P, Bullani R, Schneider P, Holler N, Salomon D, et al. Inhibition of toxic epidermal necrolysis by blockade of CD95 with human intravenous immunoglobulin. Science. 1998;282:490-3.
18. Viard-Leveugle I, Bullani RR, Meda P, Micheau O, Limat A, Saurat JH, et al. Intracellular localization of keratinocyte Fas ligand explains lack of cytolytic activity under physiological conditions. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:16183-8.
19. Parrillo SP. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Current Allergy and Asthma Reports. 2007;7:243-7.
20. Bolognia JL, Jorizzo J, Rapini R. United States of America. Elsevier. Dermatology. 2nd edition. Madrid, España: Elsevier; 2008. p. 287-300.
21. Léauté-Labrèze C, Lamireau T, Chawki D, Maleville J, Taïeb A. Diagnosis, classification and management of erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 2000;83:347-52.
22. García-Doval I, LeCleach L, Bocquet H, Otero XL, Roujeau JC. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: Does early withdrawal of causative drugs decrease the risk of death? Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:323-7.
23. Magina S, Lisboa C, Leal V, Palmares J, Mesquita-Guimarães J. Dermatological and ophthalmological sequels in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Dermatology. 2003;207:33-6.
24. Roujeau JC, Stern RS. Severe cutaneous adverse reactions to drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:1272-85.
25. Wolkenstein P, Revuz J. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Dermatol Clin. 2000;18:485-95.
26. Crosi A, Borges S, Estévez F. Reacciones adversas medicamentosas graves: síndrome de Stevens-Johnson y necrólisis epidérmica tóxica. Rev Med Uruguay. 2004;20:172-7.
27. Vanfleteren I, VanGysel D, DeBrandt C. Stevens-Johnson syndrome: A diagnostic challenge in the absence of skin lesions. Ped Dermatol. 2003;20:152-6.
28. Sheridan RL, Liu V, Anupindi S. Case 34-2005: A 10-year-old girl with a bullous skin eruption and acute respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2057-66.
29. Quinn AM, Brown K, Bonish BK, Curry J, Gordon KB, Sinacore J, et al. Uncovering histologic criteria with prognostic significance in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Arch Dermatol. 2005;141:683-7.
30. Ringheanu M, Laude TA. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in children: An update. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2000;39:687-94.
31. Bastuji-Garin S, Fouchard N, Bertocchi M, Roujeau JC, Revuz J, Wolkenstein P. SCORTEN: A severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2000;115:149-53.
32. Vaishampayan S, Das A, Verma R. SCORTEN: Does it need modification? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:35-7.
33. Sheridan RL, Weber JM, Schulz JT, Ryan CM, Low HM, Tompkins RG. Management of severe Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in children. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:497-500.
34. Schulz JT, Sheridan RL, Ryan CM, MacKool B, Tompkins RG. A 10-year experience with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Rehabil. 2000;21:199-204.
35. Fromowitz J, Ramos-Caro F, Flowers F. Practical guidelines for the management of toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:1092-4.
36. Chave TA, Mortimer NJ, Sladden MJ, Hall AP, Hutchinson PE. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: Current evidence, practical management and future directions. Br J Dermatol. 2005;153:241-53. 3
7. Pirrung MK. Management of toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Intraven Nurs. 2001; 24:10712.
38. Arevalo JM, Lorente JA. Skin coverage with Biobrane biomaterial for the treatment of patients with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20:406-10.
39. van der Meer JB, Schuttelaar ML, Toth GG, Kardaun SH, Beerthuizen G, de Jong MC, et al. Successful dexamethasone pulse therapy in a toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) patient featuring recurrent TEN to oxazepam. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001;26:654.
40. Tripathi A, Ditto AM, Grammer LC, Greenberger PA, McGrath KG, Zeiss CR, et al. Corticosteroid therapy in an additional 13 cases of Stevens-Johnson syndrome: A total series of 67 cases. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2000;21:101-5.
41. Enk A, European Dermatology Forum Guideline Subcommittee. Guidelines on the use of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin in dermatology. Eur J Dermatol. 2009;19:90-8.
42. Prins C, Kerdel FA, Padilla RS, Hunziker T, Chimenti S, Viard I, et al. Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins: Multicenter retrospective analysis of 48 consecutive cases. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:26-32.
43. Metry D, Jung P, Levy ML. Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in children with SJS and TEN: Seven cases and review of the literature. Pediatrics. 2003;112:1430-6.
44. Schneck J, Fagot JP, Sekula P, Sassolas B, Roujeau JC, Mockenhaupt M. Effects of treatments on the mortality of Stevens-Johnsons syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: A retrospective study on patients included in the prospective EuroSCAR Study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:33-40.
45. Arevalo JM, Lorente JA, González-Herrada C, Jiménez-Reyes J. Treatment of toxic epidermal necrolysis with cyclosporin A. J Trauma. 2000;48:473-8.
46. Furubacke A, Berlin G, Anderson C, Sjöberg F. Lack of significant treatment effect of plasma exchange in the treatment of drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis? Intensive Care Med. 1999;25:1307-10.
Cómo citar
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |